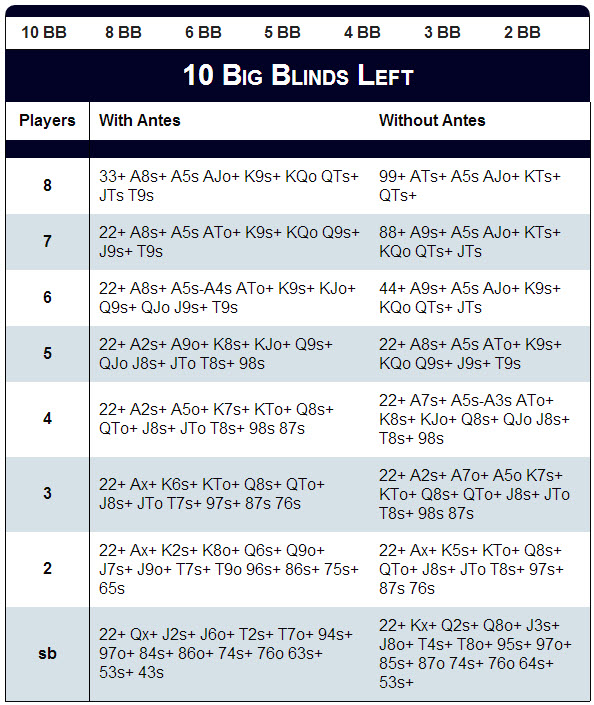
The push/fold strategy is a major weapon if it is used in the right way and at the right times. There are far too many players who will try to push/fold when it is either too early in the tournament, or before their stack size warrants the play. Be careful and selective with how you apply push/folding to your skill set. Push to Force Folds. Mathematically gifted poker minds have created Push/Fold strategy for Spin and Go poker. Below I've outlined example Push/Fold ranges for different effective stack sizes at both the button and the small blind. Remember, effective stack is the maximum amount you can go all-in against a remaining player.
Introduction
Welcome to Poker Copilot's Essential Strategy series, where we take a look at tactics, techniques, and concepts you'll need to understand if you want to become a winning poker player.
Today's post is about push/fold strategy – an approach that is crucial to understand and apply if you want to be successful at tournament poker.
Push/fold strategy is basically an 'all or nothing' pre-flop mindset that a player goes into when their chip-stack is depleted to 10 x big blinds or below.
In a tournament, if the blind levels are 75/150 and you're sitting with a stack of $1,480, it is time to stop thinking about limping, calling, or 3-betting preflop and consider each decision as either a fold or a shove.
Don't let this simple explanation fool you into thinking that the concepts or mathematics behind this strategy are irrational – there is a very sound logic that drives this approach and many factors that should determine which one of these two options you choose.
Let's start by looking at the principles and benefits of this approach.

Why Adopt This strategy?
(Source: stock.adobe.com)
In this section, we're not looking at the finer points of what choice to make. There will be many factors that drive whether we push or fold, and in many cases, there will also be a definitive mathematical justification for the right call. For now, however, we're going to keep it simple and just look at the basic principles of this strategy.
You're Using Your Stack Effectively
When you're at a stage in the tournament where the blinds represent more than 10% of your stack, it makes sense that having everyone at the table fold to you is a very positive outcome.
Let's look at this scenario.
Your stack is worth $2,900 and the blinds are 150/300. Six players left in the tournament with the top five places getting into the money (this is a scenario referred to as the bubble).
Even without there being any limpers ahead of you, getting both blinds to fold to you results in a very welcome $450 in chips!
What are the chances of the big blind folding to you if you make a bet of $750 here? Well, if the player has a stack of $4,100, he may not think twice about calling you with quite a wide range of hands and unless you have the nuts, you do not want to take the chance on a coin flip on the bubble.
However, what are the chances of him calling you if you go all-in? Will he risk 70% of his stack with A4s? That is very unlikely in this scenario.
Don't get us wrong here, we're not advocating shipping with absolute trash just because you think the rest of the players at the table are playing conservatively. Simply realize that if you have a hand that you'd ordinarily bet with, it's always a better decision to shove.
You're Getting Maximum Value
(Source: stock.adobe.com)
In some cases when you're applying the push/fold strategy, you're going to get called wide by players who think you're being reckless. This is a very good position to be in. When you find yourself with KK on the button you definitely want to be called by someone who thinks you're just trying to steal the blinds.
What you do not want to do is give your opponent the opportunity to check/fold the flop when they don't hit with their QTs. When you're short-stacked, you want to get paid with your premium hands and adopting an aggressive approach here helps create a very helpful image of being loose – something that makes getting called by weaker hands all then more likely.
Doubling up when you're short-stacked is the most effective way to get yourself back into a winning position; picking up the blinds every five or six hands will only get you so far.
What to Bear in Mind
There are many resources online that offer extremely helpful, if not downright essential, push/fold charts, online calculators, and tools that offer the information you need, but it's still important to understand the basics here.
We highly recommend you have these on hand when playing your next tournament since they offer a mathematically sound guide on the cards that you should push or fold with in various situations.
Having said that, it is essential that you understand the reasoning behind these decisions. So let's take a look at the factors that you should be taking into consideration when deciding whether you should push or fold.
Your Cards
When it comes down to it, the rules of poker and probability still apply whether you're playing a standard or a push/fold game.
The math behind the push/fold strategy takes your probability of winning if you get called into consideration, so it's essential that you don't get into the habit of thinking that you're only trying to get your opponents to fold.
Your shove is going to get called. Regularly. And when it does, you want to be ahead more often than you're not. This is where the push/fold charts we mentioned above comes into play.
Your Position
As a rule, the more players who folded out of the hand before you, the wider your range for pushing should become.
The reasoning behind this rule is simple. Even though you're playing a different strategy than traditional poker, you still need to base your decisions on all the information that your opponents are giving you about the strength of their hands. And the more who players acted before you, the more information you're getting about who you're potentially going up against in a showdown.
This also takes into consideration the number of players who still have to act after you – the fewer there are, the stronger your hand becomes.
When there are only four players left at the final table, you're not going to be thinking in terms of your position relative to the button anymore. Terms like 'under the gun', and 'cutoff' become irrelevant in this scenario.
This is the reason certain push/fold charts don't refer to position, but rather the number of players who still need to act after you.
Limpers Ahead of You

(Source: stock.adobe.com)
Nothing in life is simple, right?
Sadly the math behind those invaluable push/fold charts is based on you being the first to enter the pot voluntarily. That means a limper (a player who enters the pot by calling rather than raising) or two makes referencing a chart pointless.
Does that mean you're always folding when there was a limper ahead of you? Absolutely not! But your play is going to be reliant on some good, old-fashioned observation.
Reevaluate your decision based on what you know about the limper. Do not make a marginal shove against someone who you don't have any data on. Ideally, you'll have a poker heads-up display (HUD) such as Poker Copilot installed to track your opponent's preflop playing style and you'll have some knowledge about their VPIP range.
In the absence of this data, you'll need to have paid attention to all your opponents' preflop play before making this decision. Don't shove over a limp if you don't have any type of read on your opponent.
How many times have you seen them limp into a pot before? What was their stack size? Did they fold to a continuation bet? Did they see the river? And, most importantly, what were they holding?
It is crucial that you can answer the majority of these questions before shoving with a marginal hand – a limper severely reduces the strength of your cards.
Table Dynamics
There are going to be specific scenarios where following the push/fold strategy to the letter may not be ideal and following your read of a certain player's temperament as well as the mood at the table may be more prudent.
As you near the bubble, you might get a read on certain players getting extremely aggressive or impatient, shoving regularly in an effort to either double up or scare their opponents. If you feel like it's a matter of time before someone is called on their wide shoves, by all means, tighten up and ride out the storm.
Making the money when you're short-stacked should be your number one goal and if the action at the table tells you that the bubble is about to burst, a good case can be made for letting it happen without you risking it all.
Your Opponents' Stack Sizes
It will happen frequently that you will be in push/fold mode but have more than one player at the table with significantly fewer chips than you.

In this situation, it is often again a good move to tighten up and wait for their extremely wide pushes to get called, or for the blinds to eat away at their stacks.
Playing Against the Push/Fold Strategy
So what do you do when you're dealt a hand that you're planning to go all-in with, but you're beaten to it by another player? Do you call with the same range of hands that you'd push with?
This is again extremely dependent on your read of the player and paying attention throughout the session is crucial. Alternatively, use a HUD to build data on your opponent's preflop aggression levels.
The benefit of using a tool such as Poker Copilot is that any previous tournament you faced that particular player will be factored into the statistics the HUD displays, making your 'read' on him even more accurate.
If you want to take a slightly more binary approach to this conundrum, you can use Independent Chip Model (ICM) equity numbers to calculate whether or not a call is profitable.
Poker Strategy Push Fold Chart
Since equity and pot odds are calculated based on the monetary value of the pot you're going to win (in the case of cash games) and since tournament pot sizes aren't a 1:1 reflection of real-currency value, how do you work out what the real-world value of your chips are?
The ICM offers a solution to this question and if you are the type of player who likes to base your decisions on cold, hard data, it is critical that you understand it and how to apply it in the heat of battle. Click here to read more on this topic.
The Math
(Source: stock.adobe.com)
If you're inclined to understand the finer points of the thinking behind the push/fold strategy, read up on John Nash and how his work in the field of game theory influenced games of chance, manipulation, and strategy.
It is because of this Nobel Prize-winning mathematician and economist's remarkable work in this field that people were able to compile push/fold charts and also the reason they are often called 'Nash equilibrium charts'.
Read more on Nash's theorem and how you can use it to your advantage by clicking here.
Conclusion
Push/fold strategy is arguably the closest a poker player is going to get to playing the game according to a model that defines their actions for them. This may or may not appeal to your sensibilities as a poker player, but the benefit of applying this approach is undeniable.
Having said that, nothing beats having a solid read on your opponents in addition to working according to a solid statistical framework that guides your actions.
Avoid becoming too mechanical in your decision-making and continue paying close attention to every person at your table or install a HUD to ensure that your reads are solid.
Thanks for reading our guide to playing a push/fold strategy.
See you at the tables!
A Strong All-in Or Fold Skillset Is A Building Block Of MTT Success
– This Article Covers The Basics
There are often situations late in poker tournaments where stack sizes reduce your decisions to shove all-in (or maybe call someone else's all-in) or fold.
Sometimes you will be short-stacked, sometimes your opponent in the hand will be – and still other times, especially in turbo events, everyone will have relatively shallow stacks. In these situations you can make a superior knowledge of push / fold strategy a profitable edge, maximizing your chances of a deep run. This article breaks down the subject of all-in play in online poker tournaments, explaining the thinking behind this strategy and the common situations in which you will use it.
I will start by highlighting some situations in which post-flop play becomes difficult and the factors which go into spotting these. Next I'll cover the ‘unexploitable' all-in, and then bring in the important idea of whether shoving is optimal as well as unexploitable. Opponent types come next – this is especially relevant for lowest buy-in events, where you will meet many inexperienced players. Finally I will introduce equity math, in the form of ICM, which shows a completely different way of analyzing late-game situations.
Push / Fold Strategy For Poker Tournaments – When Post Flop Play Becomes Difficult
As your stack becomes short the flexibility you have for post-flop play quickly diminishes – for example you can not play a flop with the intention of betting again on the turn if your bet is too small to make anyone fold!
There are a few different stack sizes to cover here, each with their own strategy considerations. These are less than 12 times the big blind, less than 17 times and less than 22 times. To save this article reaching too many pages in length I have summarized each size, and then put an example underneath the 'Click Here' for readers who would like to read these.
With 12 or less big blind stacks
Here you can not open raise a pot without risking ‘committing' your whole stack. Re-raises (or calls, then reraises) will give you such huge pot-odds to call that you should rarely turn them down. However, if you would prefer not to risk your stack with a mid-strength hand then shoving all-in will often show a similar profit, with lower risk! Click Here To See / Hide Example ...
Here is a simple situation which I have used before in other articles. You have 10 big blinds, say 10000 chips with blinds at 500 / 1000 and a 50 chip ante. The pot pre flop is 2000 (assume 10 players, I like to keep the numbers rounded) and you decide to raise to 2.5 times the big blind – so, 2500 chips, with a hand which you consider worth raising, though not a premium holding.
Unfortunately, the player next to act shoves all-in, he also had 10k chips and so the pot grows to 2000 (blinds + antes) + your 2500 raise + 10,000 re-raise from the other player = 14,500. You have to call the remaining 7,500 chips in your stack to win 14,500 more, those are odds of just a tiny bit under 2-1. This makes your break-even point 35%, that is to say, if you win the hand more than 1/3rd of the time you will show a profit.
Now, the problem here is that your ‘good but not great' hand (say 77 or A10o) will win more than this against the range your opponent might re-raise with (say most pairs, ace-9+ and some KQ / KJ combinations). However, ideally, having played the tournament for 5 hours to get here, you would rather not be risking it all in such an unclear situation.
Rewind for a moment here, your error was with the initial raise. Since you did not have enough chips to play post-flop (if you were flat-called the pot on the flop would have been 7500, and any more bets would have committed you!). At this point you should abandon ideas of post-flop play and choose to either raise all-in, or fold.
This has the advantage of giving you plenty of chips (2500), without too big a risk – since your opponents will be folding most of the hands that they would have re-raised all-in with. As long as you balance the hands you do this with (if you push ‘average hands' and limp or small-raise with aces, then observant opponents will quickly pick up on this and start exploiting you!).
With 17 or less big blind stacks
Here you could raise and then fold. The problem with this stack size is that smart players will know you can not call a re-raise without getting yourself committed to the pot on all but the most dangerous of flops. They can thus re-raise as a semi-bluff, knowing your choices are to shove or fold – pressure you could do without. An additional danger lurks where you have a passive table, a couple of calls behind you can lead to a big pot in which you have little idea of where you stand. Here is an example of how easily you can hit a high pressure situation with a 15 big blind stack. Click Here To See / Hide Example...
Using the same 500/1000 blinds and an ante of 50, you decide to raise in later position to 2250 of your 15000 stack. A big stacked player behind you now raises to 5750 and everyone else folds. You now see a pot of 2000 (blinds / antes) + 2250 (your raise) + 5750 (re-raise) for 10,000 total, your remaining stack is 12500 chips. If you call the re-raise the pot is now bigger than your stack… Your choices at this point in the hand are to use your remaining fold equity by shoving (though you are likely to get called since you are offering close to 2-1 to your opponent) or to fold, any call will mean you have no idea where you stand post flop and would be the worse course of action for most of your legitimate but non-premium raising range.
This stack size might seem too big to open-shove with, but this can still be a profitable move. With tight players behind you (not too many, ideally) then the amount of times you get called will be tiny, and you will still win 30% or so of those times as long as you are not pushing complete trash.
15 big blind stacks are far better for restealing, see my main MTT strategy page for articles covering this important topic
With 22 or less big blind stacks
Here you do have some more flexibility in post-flop play, though not a huge amount. It is still possible to find ‘unexploitable' ranges for your all-ins with this kind of stack, and against the very worst opponents who call anything and re-steal super-light there are situations where you might want to do this.
The most common situation for shoving will be to pick up a raised pot before the flop. For example a looser player makes it 2.5x, another loose player calls and you have a reasonable hand in late position (though not one you would be happy to play post flop when relatively shallow stacked). Here a shove will win a 6.5x pot a good percentage of the time. While this should be a weapon in every player's armory, you need to ensure you do not only do this with a predictable ‘mid strength' range – once this is obvious, good opponents will be happy to exploit it by loosening their calling ranges just enough to profit!
My Pick For Super-Soft Poker Tournaments!
Unexploitable All-In Play In Tournaments – What Is This And How Is It Calculated?
It might surprise some readers, but there are many situations in poker tournaments in which you could turn your hand face up, shove all your chips into the pot, and still have a positive expectation in terms of chips! This is a little theoretical to start with, but has important implications for many real situations.
Why Adopt This strategy?
(Source: stock.adobe.com)
In this section, we're not looking at the finer points of what choice to make. There will be many factors that drive whether we push or fold, and in many cases, there will also be a definitive mathematical justification for the right call. For now, however, we're going to keep it simple and just look at the basic principles of this strategy.
You're Using Your Stack Effectively
When you're at a stage in the tournament where the blinds represent more than 10% of your stack, it makes sense that having everyone at the table fold to you is a very positive outcome.
Let's look at this scenario.
Your stack is worth $2,900 and the blinds are 150/300. Six players left in the tournament with the top five places getting into the money (this is a scenario referred to as the bubble).
Even without there being any limpers ahead of you, getting both blinds to fold to you results in a very welcome $450 in chips!
What are the chances of the big blind folding to you if you make a bet of $750 here? Well, if the player has a stack of $4,100, he may not think twice about calling you with quite a wide range of hands and unless you have the nuts, you do not want to take the chance on a coin flip on the bubble.
However, what are the chances of him calling you if you go all-in? Will he risk 70% of his stack with A4s? That is very unlikely in this scenario.
Don't get us wrong here, we're not advocating shipping with absolute trash just because you think the rest of the players at the table are playing conservatively. Simply realize that if you have a hand that you'd ordinarily bet with, it's always a better decision to shove.
You're Getting Maximum Value
(Source: stock.adobe.com)
In some cases when you're applying the push/fold strategy, you're going to get called wide by players who think you're being reckless. This is a very good position to be in. When you find yourself with KK on the button you definitely want to be called by someone who thinks you're just trying to steal the blinds.
What you do not want to do is give your opponent the opportunity to check/fold the flop when they don't hit with their QTs. When you're short-stacked, you want to get paid with your premium hands and adopting an aggressive approach here helps create a very helpful image of being loose – something that makes getting called by weaker hands all then more likely.
Doubling up when you're short-stacked is the most effective way to get yourself back into a winning position; picking up the blinds every five or six hands will only get you so far.
What to Bear in Mind
There are many resources online that offer extremely helpful, if not downright essential, push/fold charts, online calculators, and tools that offer the information you need, but it's still important to understand the basics here.
We highly recommend you have these on hand when playing your next tournament since they offer a mathematically sound guide on the cards that you should push or fold with in various situations.
Having said that, it is essential that you understand the reasoning behind these decisions. So let's take a look at the factors that you should be taking into consideration when deciding whether you should push or fold.
Your Cards
When it comes down to it, the rules of poker and probability still apply whether you're playing a standard or a push/fold game.
The math behind the push/fold strategy takes your probability of winning if you get called into consideration, so it's essential that you don't get into the habit of thinking that you're only trying to get your opponents to fold.
Your shove is going to get called. Regularly. And when it does, you want to be ahead more often than you're not. This is where the push/fold charts we mentioned above comes into play.
Your Position
As a rule, the more players who folded out of the hand before you, the wider your range for pushing should become.
The reasoning behind this rule is simple. Even though you're playing a different strategy than traditional poker, you still need to base your decisions on all the information that your opponents are giving you about the strength of their hands. And the more who players acted before you, the more information you're getting about who you're potentially going up against in a showdown.
This also takes into consideration the number of players who still have to act after you – the fewer there are, the stronger your hand becomes.
When there are only four players left at the final table, you're not going to be thinking in terms of your position relative to the button anymore. Terms like 'under the gun', and 'cutoff' become irrelevant in this scenario.
This is the reason certain push/fold charts don't refer to position, but rather the number of players who still need to act after you.
Limpers Ahead of You
(Source: stock.adobe.com)
Nothing in life is simple, right?
Sadly the math behind those invaluable push/fold charts is based on you being the first to enter the pot voluntarily. That means a limper (a player who enters the pot by calling rather than raising) or two makes referencing a chart pointless.
Does that mean you're always folding when there was a limper ahead of you? Absolutely not! But your play is going to be reliant on some good, old-fashioned observation.
Reevaluate your decision based on what you know about the limper. Do not make a marginal shove against someone who you don't have any data on. Ideally, you'll have a poker heads-up display (HUD) such as Poker Copilot installed to track your opponent's preflop playing style and you'll have some knowledge about their VPIP range.
In the absence of this data, you'll need to have paid attention to all your opponents' preflop play before making this decision. Don't shove over a limp if you don't have any type of read on your opponent.
How many times have you seen them limp into a pot before? What was their stack size? Did they fold to a continuation bet? Did they see the river? And, most importantly, what were they holding?
It is crucial that you can answer the majority of these questions before shoving with a marginal hand – a limper severely reduces the strength of your cards.
Table Dynamics
There are going to be specific scenarios where following the push/fold strategy to the letter may not be ideal and following your read of a certain player's temperament as well as the mood at the table may be more prudent.
As you near the bubble, you might get a read on certain players getting extremely aggressive or impatient, shoving regularly in an effort to either double up or scare their opponents. If you feel like it's a matter of time before someone is called on their wide shoves, by all means, tighten up and ride out the storm.
Making the money when you're short-stacked should be your number one goal and if the action at the table tells you that the bubble is about to burst, a good case can be made for letting it happen without you risking it all.
Your Opponents' Stack Sizes
It will happen frequently that you will be in push/fold mode but have more than one player at the table with significantly fewer chips than you.
In this situation, it is often again a good move to tighten up and wait for their extremely wide pushes to get called, or for the blinds to eat away at their stacks.
Playing Against the Push/Fold Strategy
So what do you do when you're dealt a hand that you're planning to go all-in with, but you're beaten to it by another player? Do you call with the same range of hands that you'd push with?
This is again extremely dependent on your read of the player and paying attention throughout the session is crucial. Alternatively, use a HUD to build data on your opponent's preflop aggression levels.
The benefit of using a tool such as Poker Copilot is that any previous tournament you faced that particular player will be factored into the statistics the HUD displays, making your 'read' on him even more accurate.
If you want to take a slightly more binary approach to this conundrum, you can use Independent Chip Model (ICM) equity numbers to calculate whether or not a call is profitable.
Poker Strategy Push Fold Chart
Since equity and pot odds are calculated based on the monetary value of the pot you're going to win (in the case of cash games) and since tournament pot sizes aren't a 1:1 reflection of real-currency value, how do you work out what the real-world value of your chips are?
The ICM offers a solution to this question and if you are the type of player who likes to base your decisions on cold, hard data, it is critical that you understand it and how to apply it in the heat of battle. Click here to read more on this topic.
The Math
(Source: stock.adobe.com)
If you're inclined to understand the finer points of the thinking behind the push/fold strategy, read up on John Nash and how his work in the field of game theory influenced games of chance, manipulation, and strategy.
It is because of this Nobel Prize-winning mathematician and economist's remarkable work in this field that people were able to compile push/fold charts and also the reason they are often called 'Nash equilibrium charts'.
Read more on Nash's theorem and how you can use it to your advantage by clicking here.
Conclusion
Push/fold strategy is arguably the closest a poker player is going to get to playing the game according to a model that defines their actions for them. This may or may not appeal to your sensibilities as a poker player, but the benefit of applying this approach is undeniable.
Having said that, nothing beats having a solid read on your opponents in addition to working according to a solid statistical framework that guides your actions.
Avoid becoming too mechanical in your decision-making and continue paying close attention to every person at your table or install a HUD to ensure that your reads are solid.
Thanks for reading our guide to playing a push/fold strategy.
See you at the tables!
A Strong All-in Or Fold Skillset Is A Building Block Of MTT Success
– This Article Covers The Basics
There are often situations late in poker tournaments where stack sizes reduce your decisions to shove all-in (or maybe call someone else's all-in) or fold.
Sometimes you will be short-stacked, sometimes your opponent in the hand will be – and still other times, especially in turbo events, everyone will have relatively shallow stacks. In these situations you can make a superior knowledge of push / fold strategy a profitable edge, maximizing your chances of a deep run. This article breaks down the subject of all-in play in online poker tournaments, explaining the thinking behind this strategy and the common situations in which you will use it.
I will start by highlighting some situations in which post-flop play becomes difficult and the factors which go into spotting these. Next I'll cover the ‘unexploitable' all-in, and then bring in the important idea of whether shoving is optimal as well as unexploitable. Opponent types come next – this is especially relevant for lowest buy-in events, where you will meet many inexperienced players. Finally I will introduce equity math, in the form of ICM, which shows a completely different way of analyzing late-game situations.
Push / Fold Strategy For Poker Tournaments – When Post Flop Play Becomes Difficult
As your stack becomes short the flexibility you have for post-flop play quickly diminishes – for example you can not play a flop with the intention of betting again on the turn if your bet is too small to make anyone fold!
There are a few different stack sizes to cover here, each with their own strategy considerations. These are less than 12 times the big blind, less than 17 times and less than 22 times. To save this article reaching too many pages in length I have summarized each size, and then put an example underneath the 'Click Here' for readers who would like to read these.
With 12 or less big blind stacks
Here you can not open raise a pot without risking ‘committing' your whole stack. Re-raises (or calls, then reraises) will give you such huge pot-odds to call that you should rarely turn them down. However, if you would prefer not to risk your stack with a mid-strength hand then shoving all-in will often show a similar profit, with lower risk! Click Here To See / Hide Example ...
Here is a simple situation which I have used before in other articles. You have 10 big blinds, say 10000 chips with blinds at 500 / 1000 and a 50 chip ante. The pot pre flop is 2000 (assume 10 players, I like to keep the numbers rounded) and you decide to raise to 2.5 times the big blind – so, 2500 chips, with a hand which you consider worth raising, though not a premium holding.
Unfortunately, the player next to act shoves all-in, he also had 10k chips and so the pot grows to 2000 (blinds + antes) + your 2500 raise + 10,000 re-raise from the other player = 14,500. You have to call the remaining 7,500 chips in your stack to win 14,500 more, those are odds of just a tiny bit under 2-1. This makes your break-even point 35%, that is to say, if you win the hand more than 1/3rd of the time you will show a profit.
Now, the problem here is that your ‘good but not great' hand (say 77 or A10o) will win more than this against the range your opponent might re-raise with (say most pairs, ace-9+ and some KQ / KJ combinations). However, ideally, having played the tournament for 5 hours to get here, you would rather not be risking it all in such an unclear situation.
Rewind for a moment here, your error was with the initial raise. Since you did not have enough chips to play post-flop (if you were flat-called the pot on the flop would have been 7500, and any more bets would have committed you!). At this point you should abandon ideas of post-flop play and choose to either raise all-in, or fold.
This has the advantage of giving you plenty of chips (2500), without too big a risk – since your opponents will be folding most of the hands that they would have re-raised all-in with. As long as you balance the hands you do this with (if you push ‘average hands' and limp or small-raise with aces, then observant opponents will quickly pick up on this and start exploiting you!).
With 17 or less big blind stacks
Here you could raise and then fold. The problem with this stack size is that smart players will know you can not call a re-raise without getting yourself committed to the pot on all but the most dangerous of flops. They can thus re-raise as a semi-bluff, knowing your choices are to shove or fold – pressure you could do without. An additional danger lurks where you have a passive table, a couple of calls behind you can lead to a big pot in which you have little idea of where you stand. Here is an example of how easily you can hit a high pressure situation with a 15 big blind stack. Click Here To See / Hide Example...
Using the same 500/1000 blinds and an ante of 50, you decide to raise in later position to 2250 of your 15000 stack. A big stacked player behind you now raises to 5750 and everyone else folds. You now see a pot of 2000 (blinds / antes) + 2250 (your raise) + 5750 (re-raise) for 10,000 total, your remaining stack is 12500 chips. If you call the re-raise the pot is now bigger than your stack… Your choices at this point in the hand are to use your remaining fold equity by shoving (though you are likely to get called since you are offering close to 2-1 to your opponent) or to fold, any call will mean you have no idea where you stand post flop and would be the worse course of action for most of your legitimate but non-premium raising range.
This stack size might seem too big to open-shove with, but this can still be a profitable move. With tight players behind you (not too many, ideally) then the amount of times you get called will be tiny, and you will still win 30% or so of those times as long as you are not pushing complete trash.
15 big blind stacks are far better for restealing, see my main MTT strategy page for articles covering this important topic
With 22 or less big blind stacks
Here you do have some more flexibility in post-flop play, though not a huge amount. It is still possible to find ‘unexploitable' ranges for your all-ins with this kind of stack, and against the very worst opponents who call anything and re-steal super-light there are situations where you might want to do this.
The most common situation for shoving will be to pick up a raised pot before the flop. For example a looser player makes it 2.5x, another loose player calls and you have a reasonable hand in late position (though not one you would be happy to play post flop when relatively shallow stacked). Here a shove will win a 6.5x pot a good percentage of the time. While this should be a weapon in every player's armory, you need to ensure you do not only do this with a predictable ‘mid strength' range – once this is obvious, good opponents will be happy to exploit it by loosening their calling ranges just enough to profit!
My Pick For Super-Soft Poker Tournaments!
Unexploitable All-In Play In Tournaments – What Is This And How Is It Calculated?
It might surprise some readers, but there are many situations in poker tournaments in which you could turn your hand face up, shove all your chips into the pot, and still have a positive expectation in terms of chips! This is a little theoretical to start with, but has important implications for many real situations.
Unexploitable shoves work when there are few opponents left to act, and the blinds and antes are a big proportion of your stack. Say you turned over K-10 from the small blind, and then shoved all-in with 10 BBs.
A savvy opponent could look at the pot odds, then compare the winning chances of his hand to see whether he had enough equity to call. Most of the time he would fold (assuming your hand is not junk) and those times he does call you will have winning chances against his calling hands. So there are a few different scenarios, including the double-up.
Using the free tool PokerStove you can work out the equity of different hands compared to ‘ranges' – the rest is just calculating odds of having those hands and the chips won * percentage of the time each outcome happens.
As you add more opponents the math becomes more difficult, any more than 2 people would see the chances of someone having a calling hand grow too large to make the math work – so this is mostly a button / small blind move.
Implications Of Unexploitable Shoves
Now, since it is possible to take a mid-strength hand like K-10 - show it before you shove – and still win chips, think about how powerful adding some mystery to your holding becomes… Now your opponent needs to assess his hand against your perceived range, meaning they will not have a clear decision and will often compensate by tightening up their calling range.
A couple of caveats here; first, make sure that your opponent is experienced, bad players will often call light (great if you have a real hand!). Second, remember that your past behavior affects ranges, if you do this 3 times in a row then someone out there will be just itching to call you!
Poker Push Fold Strategy Tactics
Before you all get shove-happy in the later stages, I'd like to introduce a new concept. Even if you have an unexploitable shove, or other great all-in opportunity - there might be an even better line, which makes even more money.
Now, you need to balance your ranges somewhat. There is nothing more obvious than someone suddenly going from shove-maniac to limping or mini-raising. As long as your play is not obvious, you might want to think about whether you really want to encourage some action to win a bigger pot – or go for the all-in to (most probably) just take the blinds and the antes.
All-In / Fold Strategy In Poker Tournaments – Opponent Types, Stack Sizes And Situations
Just considering the math of your push-fold play and your own stack size will already put you ahead of the majority of your opponents. If you are aware enough to predict the behavior of opponents, work out how their stack sizes affect their judgments and spot good situations to make all-in moves, then your play in the later stages of MTTs will become downright dangerous!
Lets take those factors one-by-one:
Opponents: Some players will have nasty habits like flat calling raises (or even re-raises), floating flops (calling with nothing much to see if they can take the pot on the turn / river) or raising every time the action is folded to them in one of the later positions. By working out which opponents are capable of raise-folding and which are reluctant you already have a ‘target list' for re-steals. If there are players behind you who are too likely to flat call, and will make playing mid-strength hands difficult, then you might prefer to take the value available from a shove all-in and wait for a better spot to consider post-flop play.
Stacks: Mid-sized stacks are most likely to release their hands facing an all-in. Short stacks can often be feeling desperate, and if they think you might be stealing then they can often take a chance by calling your shove. Big stacks may have enough chips to take a shot at your stack, remember, those extra chips of yours might take their stack to a new level, where they can steal with impunity… If you choose the mid-size stacks who are currently comfortable and would only call when tight, then you have a great chance of your shove winning the blinds.
Situations: Bubble situations are the best for all-in play, here most players tend to tighten up, waiting for the money before they try adding to their stack. The final table bubble is similar, lots of experienced players now exploit bubbles – which can lead to some interesting opportunities to call ‘light' if you can stand the variance. Other situations to look out for involve players suddenly changing their plays, someone who is happy to shove suddenly mini-raising should set off alarm bells. A tight mid-sized stack making a bubble 3-bet should see you running a mile!!
My Pick For Super-Soft Poker Tournaments!
Prize Pool Equity In MTT Push-Fold Play – How About ICM?
ICM stands for the Independent Chip Model, this is a way of making poker decisions based on the average equity you hold in the prize pool of a game, rather than just the amount of chips you hold.
This is based on the fact that prizes in tournaments (or SNGs) are top-heavy. Here is a simplified example to show the math in action.
4 players, each have 1000 chips, with a $100 prize pool divided as $50 for 1st, $30 for 2nd and $20 for 3rd (4th gets nothing). I will exclude the blinds for now to keep the example easy to follow.
Over 100's of games each player can expect to win $25 here… all else being equal. In other words, their current prize pool equity is $25 each.
Now, player A raises all in to steal the blinds, and player B decides to call. Here, if player B's decision were based on chips, he would be risking 1000 chips to win 1000 more chips… so as long as he won 51% of the time, his call would be good.
If we look at the prize pool equity, a different story takes shape. Here he is risking $25 in equity – but to win what?
Well, with the maximum possible winnings being $50 we can not say he wins $25 more, since the other 2 players are still very much in the game and will win some of the time. In fact, the math shows that over 100's of games a player with 2000 the chips in the last 3 will win around $37 on average, with the other two players winning $31.50c each.
Going back to risk / reward, player B risked his $25 equity to win an average of just $12 more in equity… he would thus need to win 66% of the time that he called to make this a +ev play.
This is not some virtual currency, these decisions are in real money and cost players who misunderstand prize pool equity a lot over time. There are very few hands which are 2-to-1 favorite over a random hand in Holdem, and if you put the original shover on a tight range you quicky narrow the hands you can call with.
OK, how does this relate to the later stages of poker tournaments.
Things get more complicated in real life situations, different stack sizes, prize pools which are set up differently and so on. What you need to think about, especially at the final table, is the average value of your chips in terms of the slice of the prize pool you will win one the cards balance out (over the theoretical 100's of games). If you call an all-in at the final table then you are risking your entire prize pool equity, usually for a smaller gain in average equity – make sure that your gain is worth the potential loss.
I recommend that readers study ICM in more detail once you are familiar with the basics of push/fold tournament play. Tools like ICMIZERcan help you with the math and simulate situations in small tournaments and SNGs. Having this understanding could make a big difference to your bankroll should you hit a final table soon!
Push / Fold Strategy In Poker Tournaments – Bringing It All Together
You need to understand the factors which go into push-fold strategy, even if you make these moves only rarely yourself. There will be many times when an opponent moves their stack into the middle – and once you know how they are approaching the game you should be able to differentiate the ‘steals' from the ‘unexploitable shoves' from those time when someone is trying to look weak and really hoping to be looked up.
Tools such as Tournament Indicator will help you learn the math behind all-in situations – this one is approved by the big sites and will quickly pay for itself.
In my view experience is the key, and adding a solid all-in or fold strategy will soon be keeping you ahead of the blinds in those crucial situations approaching the final table.
Poker Push Fold Strategy Examples
Finally, remember, not all poker sites are equal in terms of the skill and experience level of your opponents – if you are not actively seeking the softest games then you are leaving profits on the tables!! For non-US readers, 888 Poker have what I consider the softest poker tournaments online - check them out for yourself at 888 Poker now!
More Beginner / Improver Poker Tournament Articles
Poker Push Fold Strategy For Beginners
Latest News – Planet Mark's SNG Planet Blog
